Understanding the role of access controls when protecting your data
Posted on April 12, 2024 • 6 min read • 1,185 wordsBest practices for safeguarding sensitive HR information using RBAC

In the modern digital era, protecting sensitive information in Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) is crucial for organizations due to concerns over data privacy and cybersecurity. Role Based Access Control (RBAC) plays a vital role in this by providing a detailed method for managing user access and keeping HRIS data secure. This article will go over the basics of RBAC in HRIS and show how it can aid organizations in safeguarding their employees’ personal information while adhering to regulations like GDPR.
Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is a crucial aspect of managing HRIS effectively, ensuring the protection of sensitive HR data. This method involves defining specific roles within an organization and assigning precise permissions to these roles based on job requirements. By doing so, access to information is strictly regulated according to job functions, enhancing efficiency and security in the digital realm.
In HRIS, RBAC operates on the principle of restricting data access according to individuals’ operational roles. For example, HR managers may need comprehensive access to employee records for their responsibilities, while department heads may need access only to information related to their team members. Through careful role mapping and access level assignment, RBAC helps maintain the integrity of HR data, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized disclosure of confidential information.
RBAC also helps in establishing a structured environment where access control is not only about permissions but also about aligning data accessibility with organizational roles. This approach ensures that the HRIS is not only secure but also optimally functional for every user, enhancing operational efficiency. By focusing on roles in data access control, RBAC serves as a strategic tool for ensuring that user interactions with the HRIS are purposeful and meaningful.
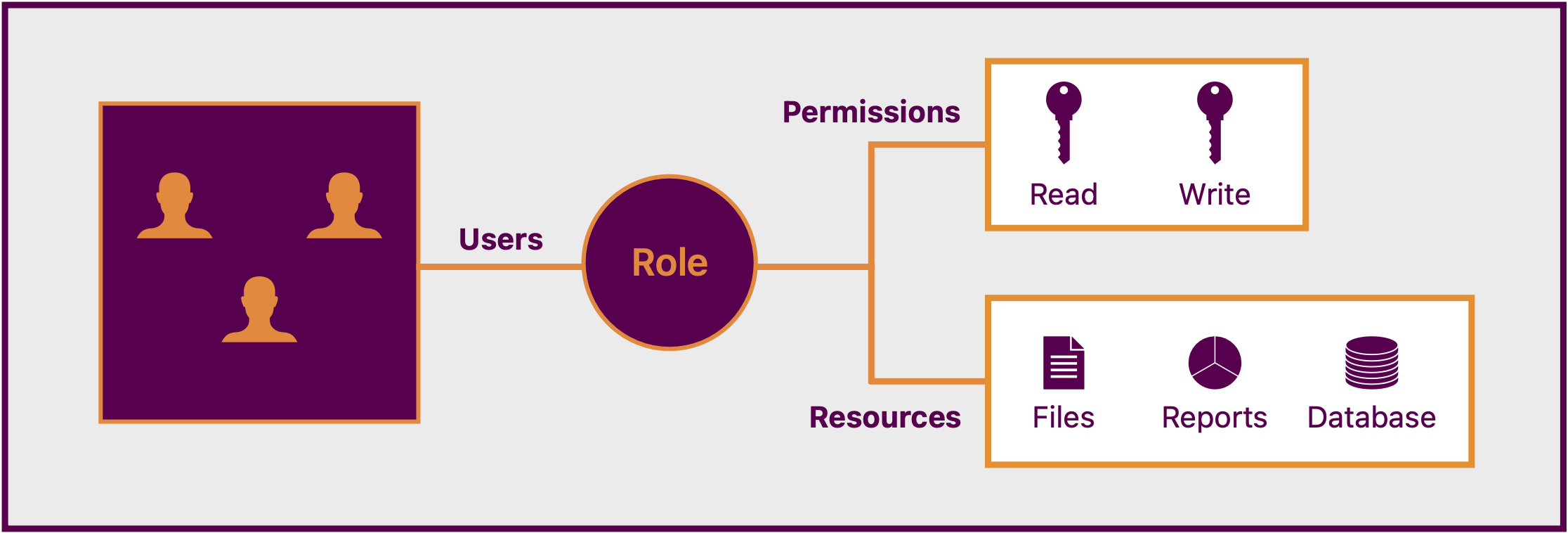
By incorporating Role Based Access Control (RBAC) into their Human Resources Information Systems (HRIS), organizations establish a strong basis for protecting data and complying with regulations. RBAC helps enforce the principles of limiting data to what is necessary and providing access only to those who need it, which are key aspects of contemporary data protection regulations. With careful implementation of RBAC, businesses can effectively manage data privacy challenges and ensure their HRIS remains secure and efficient in the digital age.
Data visibility to user needs
In HRIS management the Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is highlighted for its ability to personalize data visibility based on the specific roles and responsibilities of each user. This approach ensures that individuals only have access to relevant information, enhancing data security and operational efficiency. By defining roles and permissions meticulously, organizations can create a secure and efficient information access system.
This customization goes beyond access control, creating an ecosystem where each user’s interactions with the HRIS are tailored to their needs. For example, an employee in the payroll department would have access to financial records but be restricted from personal employee data. This precision not only protects sensitive information but also reduces information overload, allowing employees to focus on what is essential for their work.
By adopting this personalized approach to data visibility, organizations create a more focused and productive work environment. Employees do not have to sift through irrelevant information, increasing productivity and improving the user experience. RBAC in HRIS management demonstrates a commitment to security, efficiency, and personalized user experience. It transforms the way organizations and employees interact with sensitive information, making it a key element of modern HRIS management.
Permissions
Exploring RBAC in HRIS management involves distinguishing between read only and read and write permissions, which is crucial for maintaining data integrity while empowering employees appropriately. By carefully assigning these permissions, organizations ensure that only authorized personnel can make changes to information, preserving the accuracy and security of employment records and personal data. For example, HR professionals may have read and write access to update employee details or process promotions, while other employees may be limited to read only access to view information without altering any records. This level of control enhances the security and flexibility of the HRIS, allowing for adjustments to access as needed and preventing accidental data modifications. By incorporating such meticulous access permissions, organizations demonstrate a commitment to cybersecurity and data privacy, ensuring that every action in the HRIS is guided by precision and accountability. The distinction between read only and read and write permissions in RBAC exemplifies a balanced approach to user empowerment and data protection, making it an essential component of modern HRIS management.
Providing and Revoking Access
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is known for its flexibility in managing user permissions according to the changing needs of an organization’s workforce. This dynamic approach ensures that access rights are always aligned with current roles and responsibilities, enhancing security and operational efficiency. With RBAC, adjusting user access is effortless and precise. For instance, when an employee receives a promotion or switches departments, their access rights can be quickly updated to match their new role, providing them with the necessary information to excel. Conversely, if an employee leaves the company or moves to a role with reduced access requirements, their permissions can be promptly modified or revoked. This flexibility is crucial for maintaining the security of the HRIS and preventing outdated access rights from posing a risk. This agile permission management supports a proactive approach to cybersecurity, enabling organizations to respond promptly to changes without compromising data privacy. It mitigates the risk of former employees retaining access or current employees overstepping their boundaries, a key consideration in today’s data protection landscape. In summary, RBAC’s ability to dynamically grant and revoke access reflects a forward thinking strategy in data management. It ensures that an organization’s HRIS remains secure and adaptable to the evolving workforce structure, showcasing the importance and sophistication of RBAC in modern HR data management. This capability strengthens data protection measures and improves the overall functionality of the HRIS, benefiting both the organization and its employees.
Compliance and Data Privacy
In today’s digital world, it is crucial for organizations worldwide to comply with strict data protection laws such as GDPR and HIPAA. One effective way to align with these regulations is by implementing Role Based Access Control (RBAC) in HRIS systems. RBAC ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive HR data needed for their specific job roles, reducing the risk of unauthorized data exposure and potential breaches.
RBAC’s strength lies in its ability to adapt to changes in organizational structures and roles, making it a reliable guardian of data privacy. By using RBAC principles, companies can confidently navigate the complexities of GDPR compliance, demonstrating a strong commitment to data protection and building trust among employees and stakeholders.
In addition to that, RBAC’s proactive approach in managing permissions ensures data is not only protected but also handled with integrity. This level of control is essential in safeguarding personal information, making RBAC a valuable tool for achieving GDPR compliance and maintaining the security of HRIS data. By strategically implementing RBAC, organizations can strike a balance between operational efficiency and data privacy, establishing a high standard in managing sensitive HR information.